Home » Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic interactionism is an interaction between human beings via symbols such as words, definitions, roles, gestures, rituals etc. Symbolic interactionism focuses on the nature of interaction the dynamic patterns of social action and social relationship. Whatever form of interaction takes place it emerges from a particular situation. Symbolic interactionism as a concept was formulated by Herbert Blumer but given by Mead. It is a socio-psychological perspective as it focuses on small-scale interpersonal relations. In this individuals are viewed as active constructors of their own conduct to interpret, evaluate, define and map out their own actions rather than being passive persons influenced by outside forces. This approach stresses on the process by which the individuals make decisions and form opinions.
In Meadís view human thought experience and conduct are essentially social. Symbols impose particular meanings on objects and these meanings are constructed and reconstructed in the process of social interaction. Symbolic interaction is necessary since man has no instincts to direct his behavior. He is not genetically programmed to react automatically to particular stimuli. In order to survive he has to find medium of interaction with others and symbols filled the lacuna. Via symbols meaning is imposed on the world of nature and human interaction with that world is there by made possible. Mead defines a symbol as the stimulus whose response is given in advance. He argues that through the process of role taking the individual develops a concept of self. By placing himself in the position of others he is able to look back upon himself. Mead claims that the idea of a self can only develop if the individual can get outside himself in such a way so as to become an object to himself. Symbolic interactionism is an anti theoretical sociological theory that refuses in principle to transcend the peculiar characteristics of social processes. It goes towards conceptual generalization and abstraction and allowing concepts to function at best a sensitizing function. They always try to interpret a particular situation rather than a set of general situations.
Symbolic interaction was influenced by the view of Charles Horton Cooley that the sense of self is not self-generating but it is developed through interaction with significant others. In our social interaction other people act like a mirror or looking glass in which we see ourselves. What other people think of us is like a mirror image of ourselves in society. A person compares his self-image to how others perceive him.
Joel M Charon in his Symbolic Interactionism: An Introduction, An Interpretation, An Integration, 2004 highlights five characteristics of Symbolic Interaction which include the assumptions that human beings should be considered as social and thinking beings, human perceive their environments subjectively and not objectively, cause of human action lies in present and they are not passive to their environment. The crucial assumption that human beings possess the ability to think differentiates symbolic interactionism from its behaviorist roots. The ability to think enables people to act reflectively rather than just behave unreflectively. The ability to think is embedded in the mind and mind is different from physiological brain. Mind is a result of socialization process and it is not a thing but is a process.
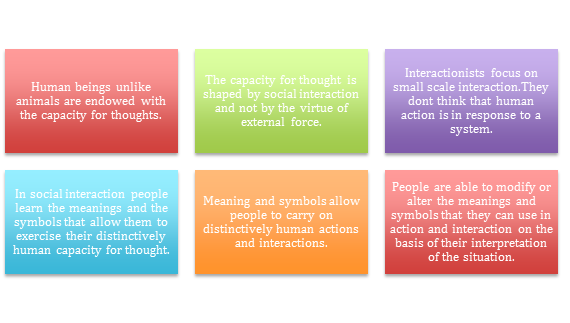
The basic principles of symbolic interaction can be as following
|
|
Symbolic interactionism is also criticized of having a narrow micro focus. It ignores certain common facts like power, structure and their constraining influence on human actions and interactions. They examine human interaction in a vacuum. They focus only on small face-to-face interaction and ignore the larger social settings. According to Skidmore interactionists fail to explain why people consistently choose to act in a given ways in certain ways instead of all possible ways. They ignore the social constraints. Symbolic interactionism embodies American values of liberty, freedom and individuality and is biased by it and deliberately ignores the harsher reality of life. Marxists argue that meanings that are generated are not a result of interaction but external force due to presence of class relationships.

 |
© 2024 Sociology Guide.Com |
 |