Home >> Marriage Family and Kinship >> Types of Marriages
Types of Marriage
Meaning and Types of Marriage
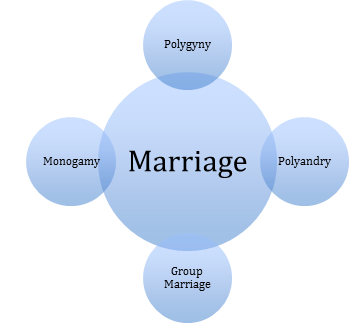
Marriage is one of the universal social institutions established and nourished by human society. It is closely connected to the institution of family. According to Gillin and Gillin, "Marriage is a socially approved way of establishing a family of procreation." Westermarck says that marriage is rooted in the family rather than the family in the marriage. Marriage is an institution of society with different purpose, functions and forms in different societies but is present everywhere as an institution. According to Malinowski, " marriage is a contract for the production and maintenance of children." According to Robert H Lowie," Marriage is a relatively permanent bond between permissible mates."The main types of marriages are:
Polygyny
Polygyny is a form of marriage in which one man married more than one woman at a given time. Polygyny is more popular than polyandry but not as universal as monogamy. It was a common practice in ancient civilizations. At present it may be present in primitive tribes like Crow Indians, Baigas and Gonds of India. Polygyny is of two types: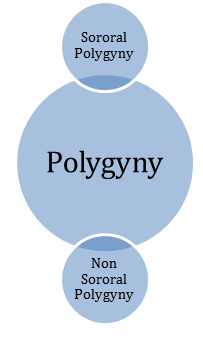
Sororal polygyny
It is a type of marriage in which the wives are invariably the sisters. It is often called sororate. The Latin word Soror stands for sister. When several sisters are simultaneously or potentially the spouses of the same man the practice is called sororate. It is usually observed in those tribes that pay a high bride price.Non-sororal polygyny
It is a type of marriage in which the wives are not related as the sisters.Polyandry
Polyandry is the marriage of one woman with several men. It is practiced among the Marquesan Islanders of Polynesia, The Bahama of Africa and tribes of Samoa. In India among tribes of Tiyan, Toda, Kota, Khasa and Ladakhi Bota it is still prevalent. Polyandry is of two.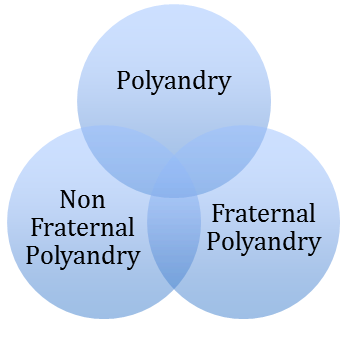
Fraternal polyandry
When several brothers share the same wife, the practice can be called fraternal polyandry. This practice of being mate, actual or potential to one's husband's brothers is called levirate. It is prevalent among the Todas in India.Non - fraternal polyandry
In this type the husbands need not have any close relationship prior to the marriage. The wife goes to spend some time with each husband. So long as a woman lives with one of her husbands, the others have no claim over her. Polyandry has its own implications. It gives rise to the problem of determining biological paternity of the child. Among the Todas one of the husbands goes through what is called a bow and arrow ceremony with the woman and thereby becomes the legal father of her child. Among the Samoans, the children after the first few years are given the liberty to choose their parents for their permanent stay. The selected parent becomes the actual father of the children.|
|
Monogamy
Monogamy is a form of marriage in which one man marries the woman. It is most common form of the marriage found among in the societies around the world. According to Westermarck monogamy is as old as humanity. Monogamy is universally practiced providing marital opportunity and satisfaction to all the individuals. It promotes love and affection between husband and wife. It contributes to family peace, solidarity and happiness. Monogamous marriage is stable and long lasting. It is free from conflicts that are commonly found in polyandrous and polygamous families. Monogamous marriage gives greater attention to the socialization of their children. Women are given very low position in polygyny where their rights are never recognized. In monogamy women enjoy better social status. There are two types of monogamy.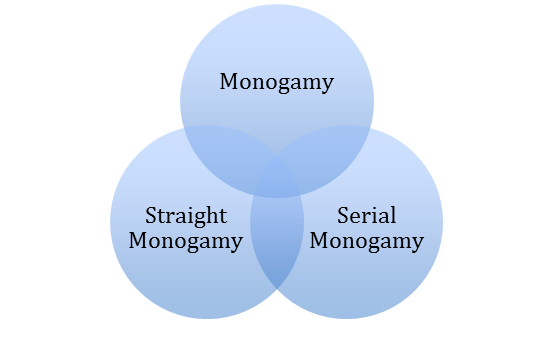
Serial monogamy
In many societies individuals are permitted to marry again often on the death of the first spouse or after divorce but they cannot have more than one spouse at one and the same time.Straight monogamy:
In straight monogamy the remarriage of the individuals is not allowed.Group Marriage
Group marriage means the marriage of two or more women with two or more men. Here the husbands are common husbands and wives are common wives. Children are regarded as the children of the entire group as a whole.
 |
© 2026 sociologyguide |
 |